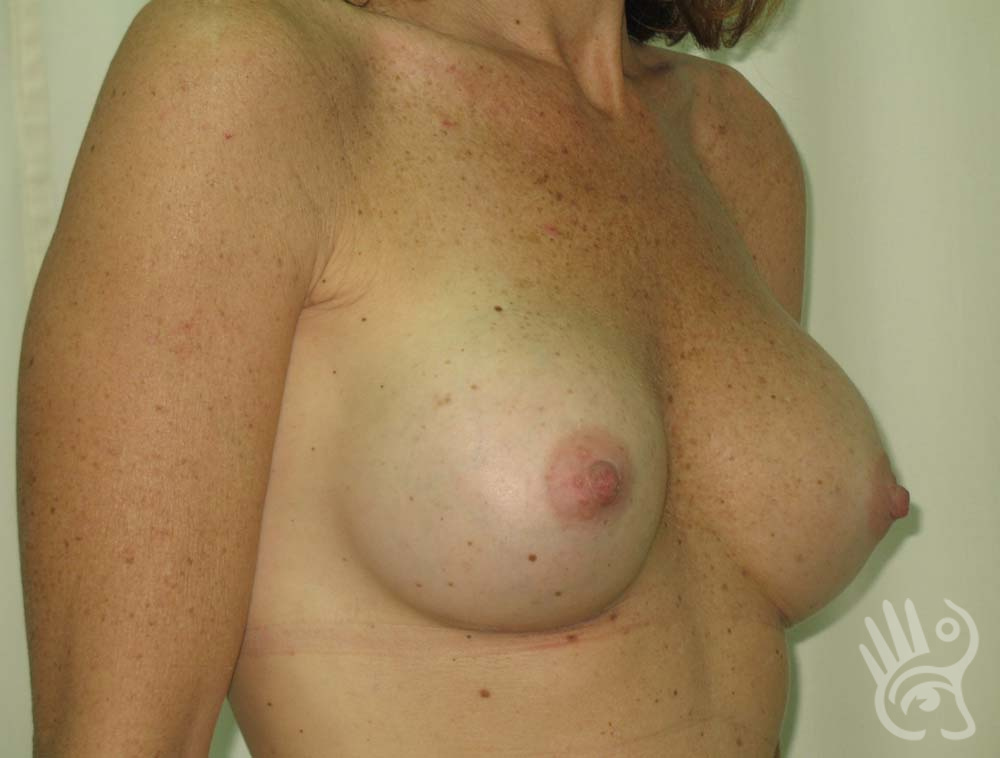
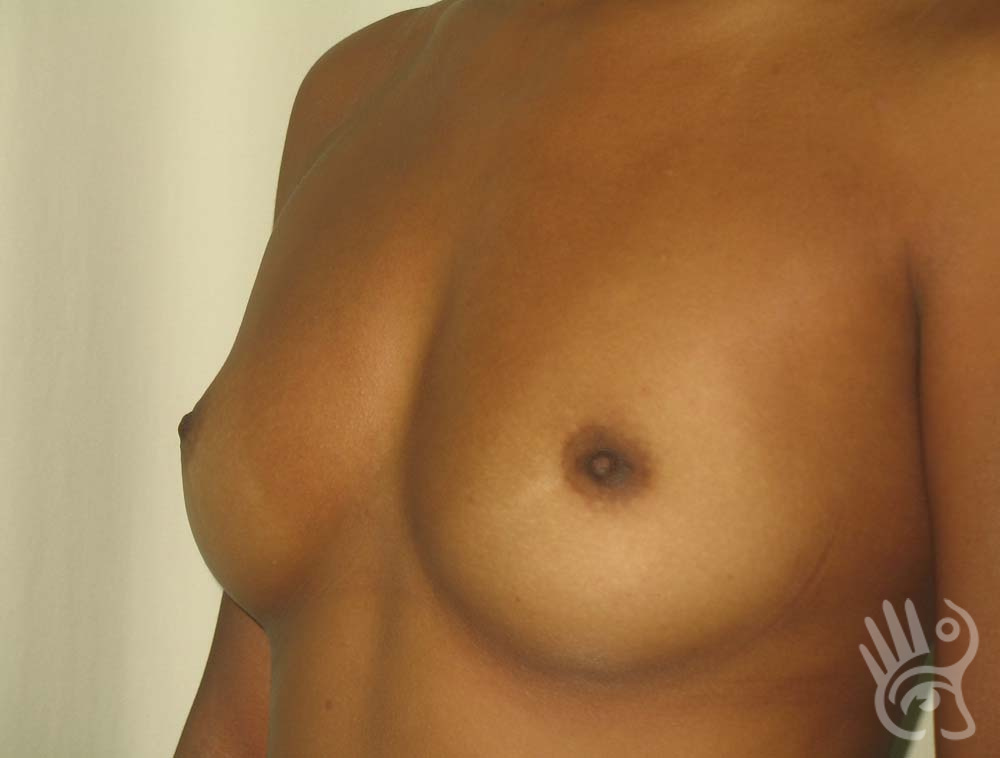
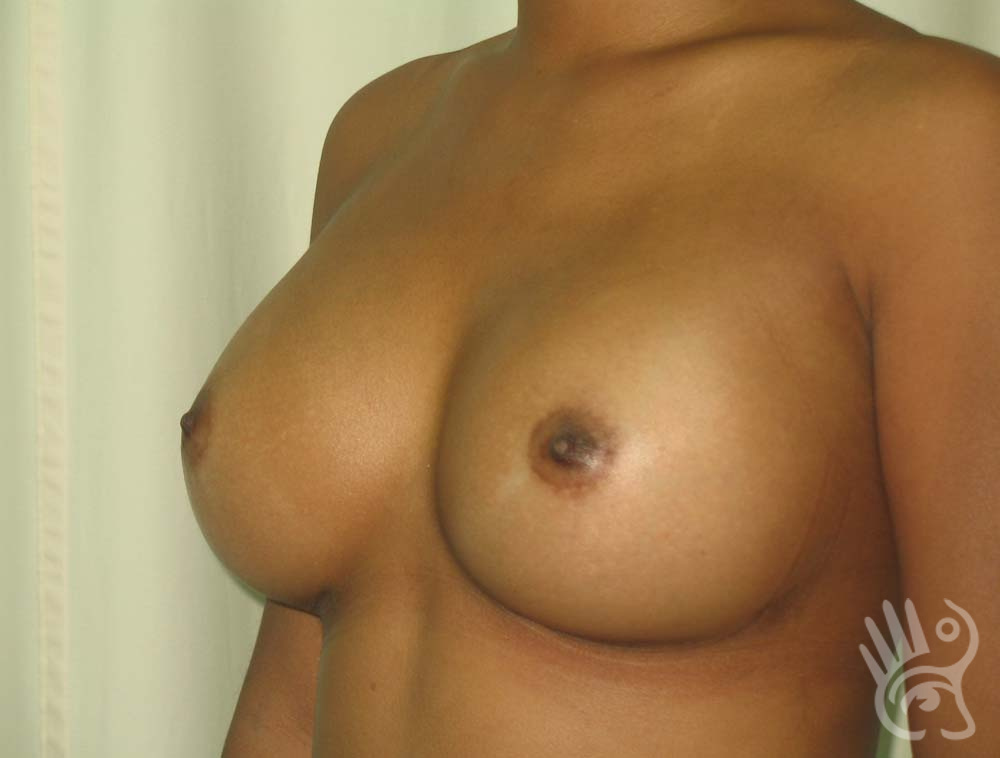
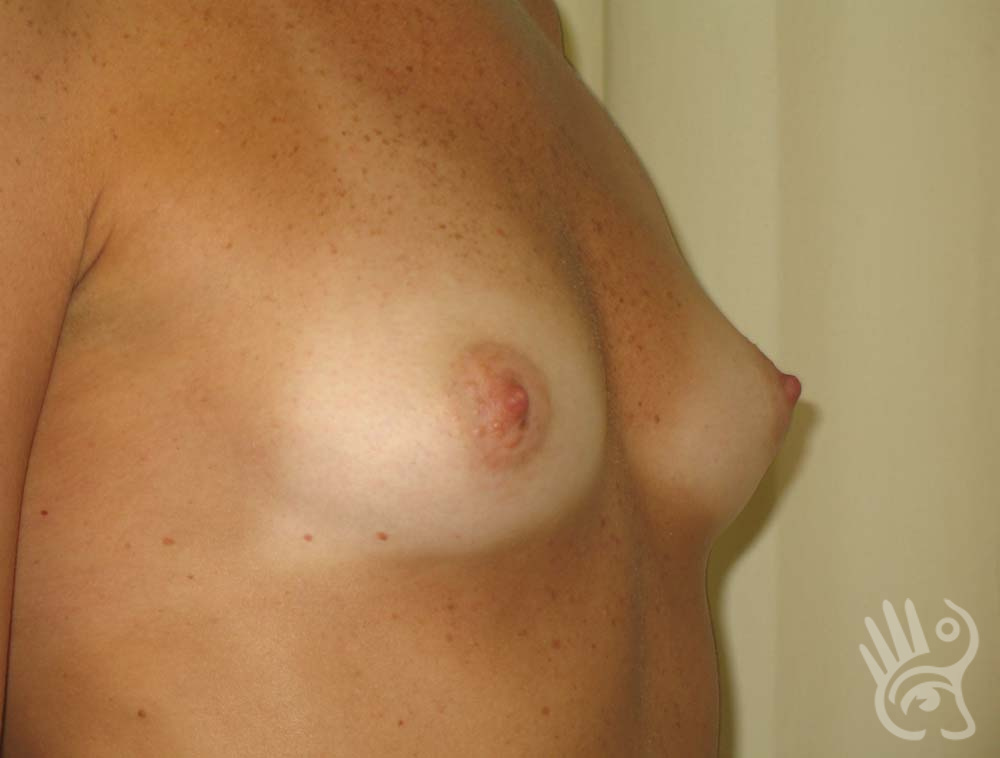
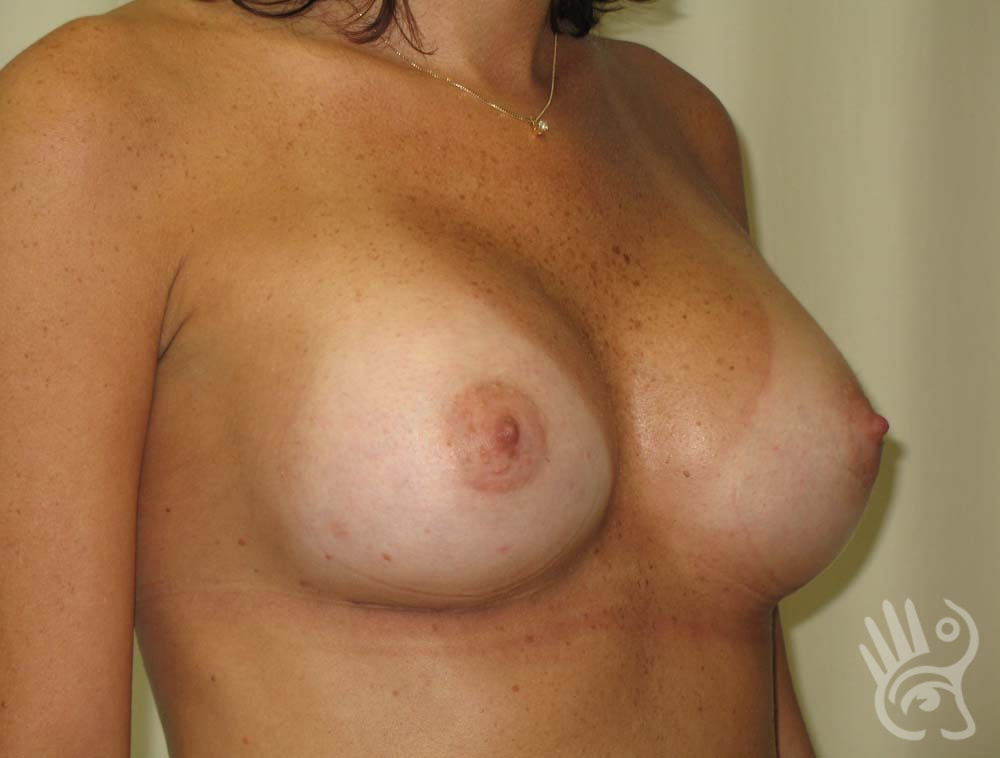
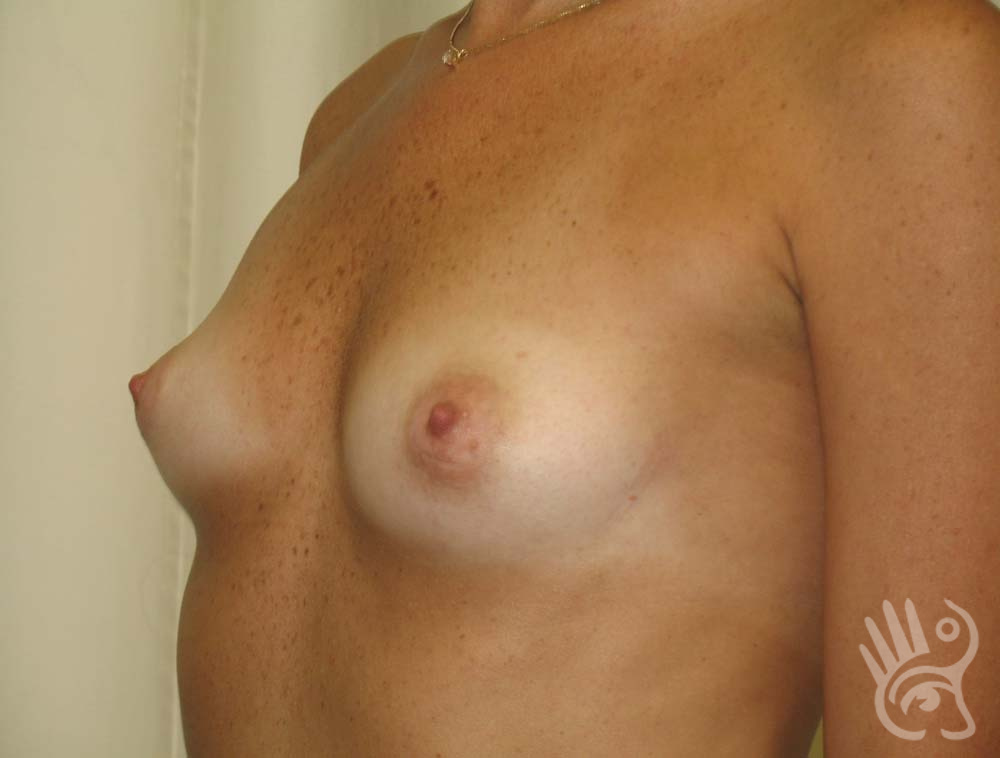
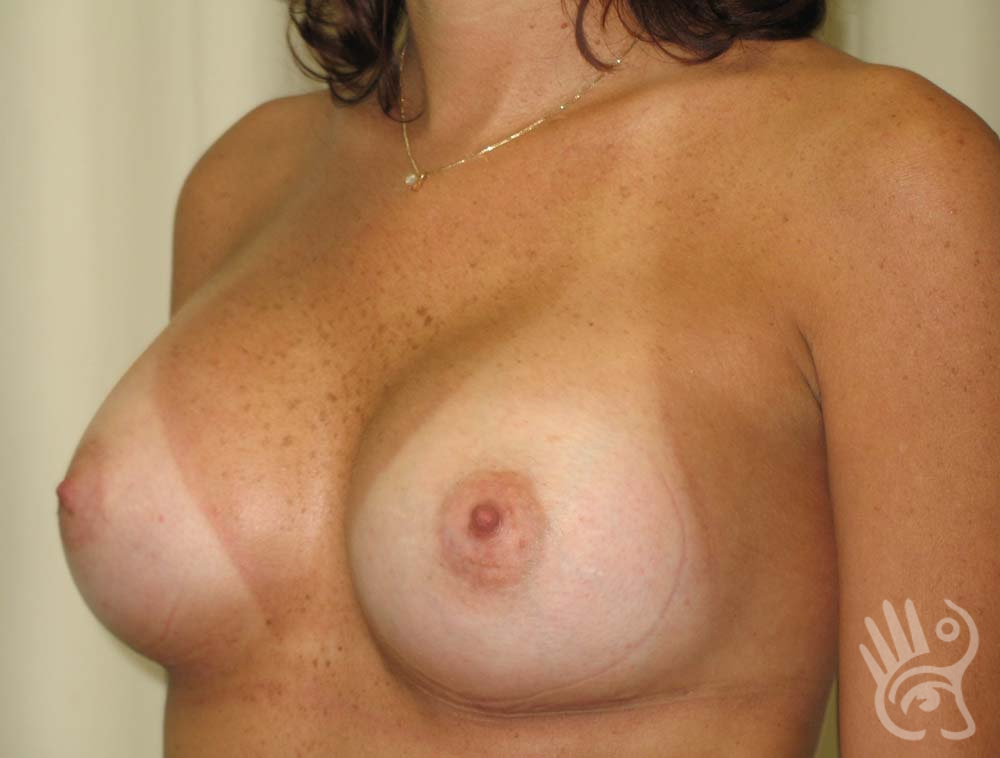
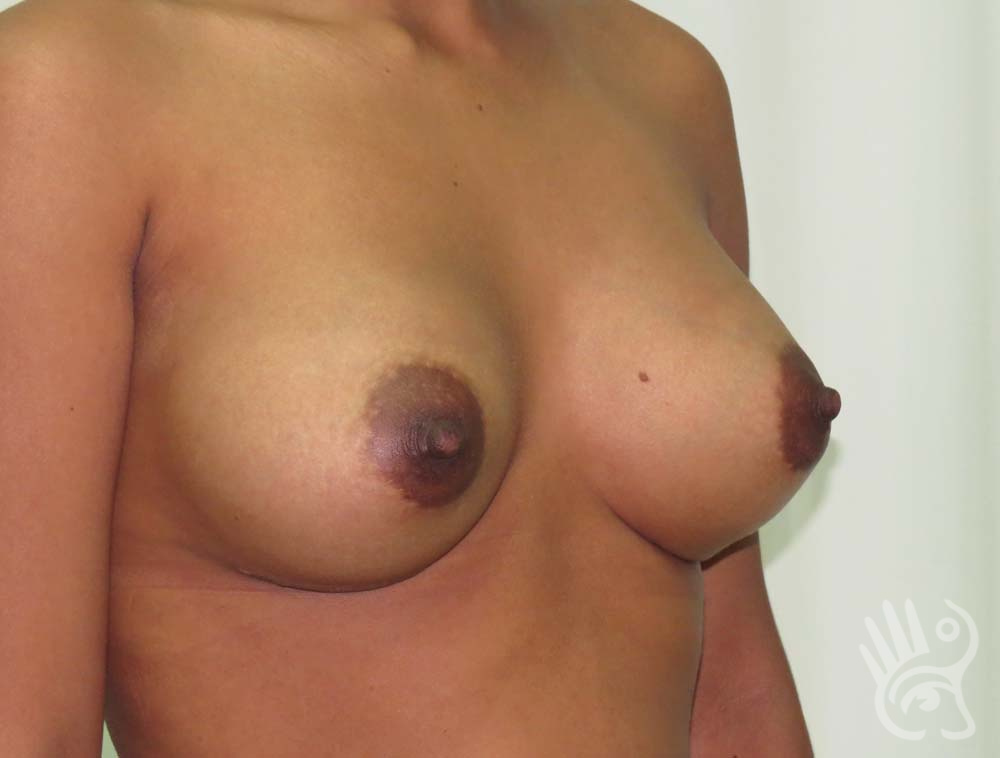
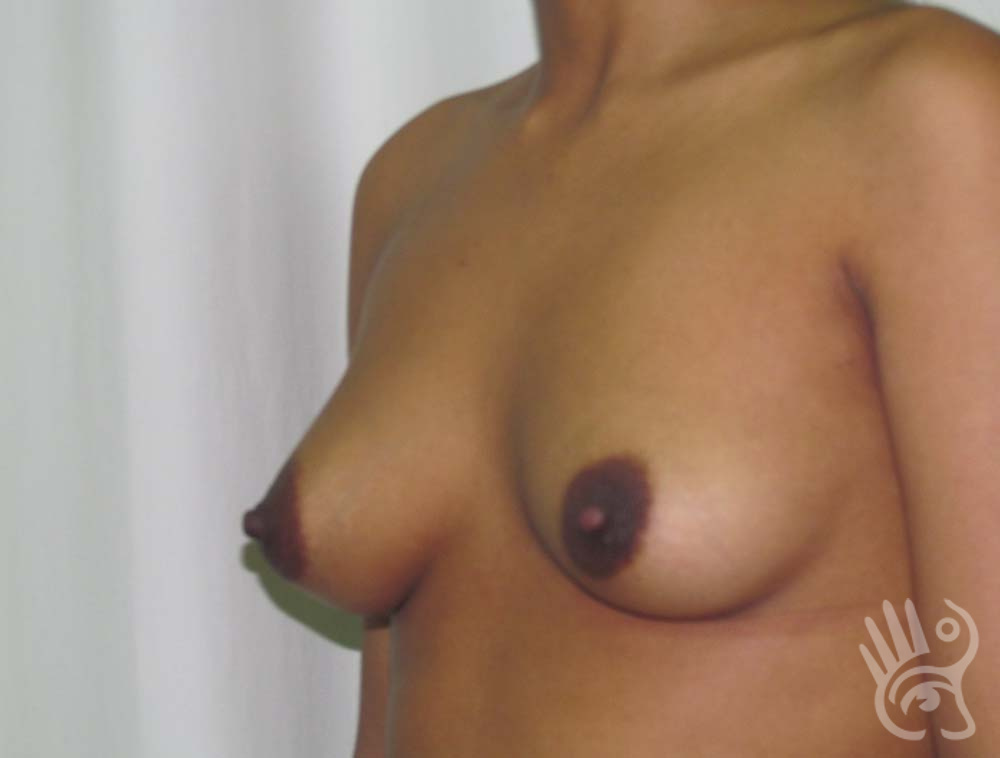
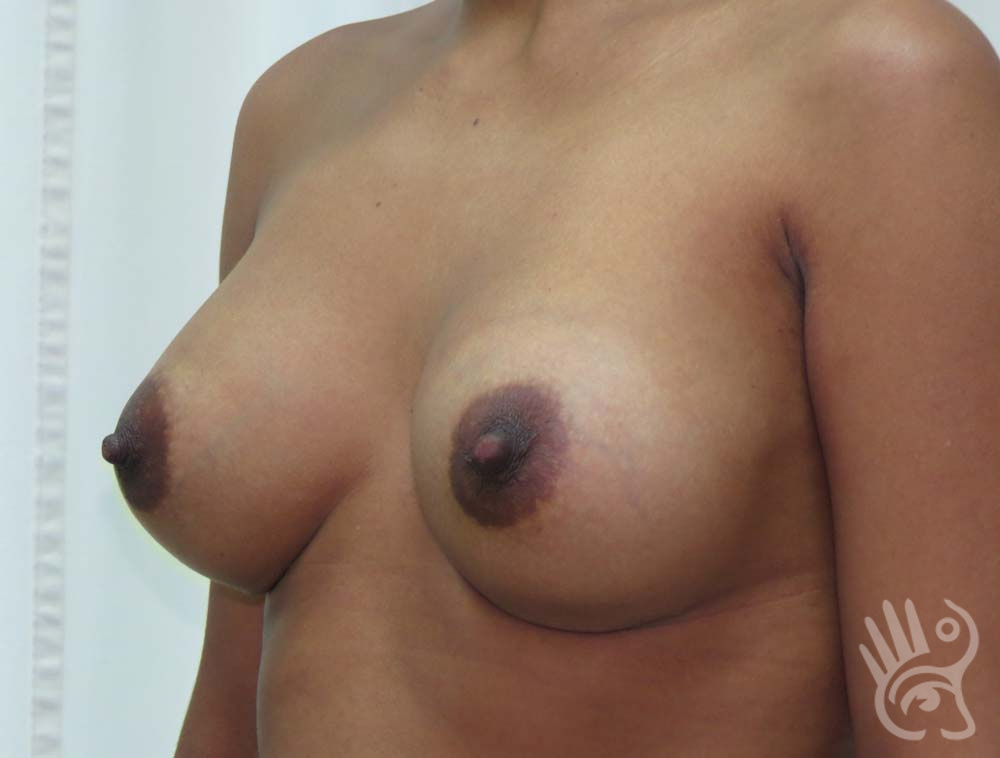
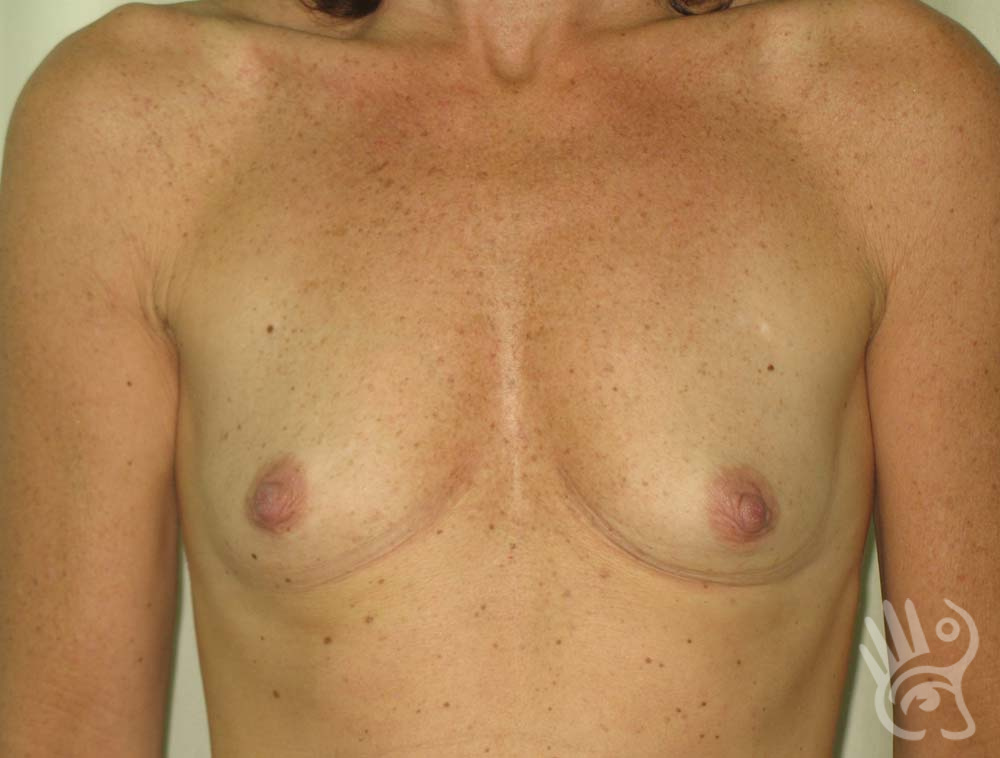
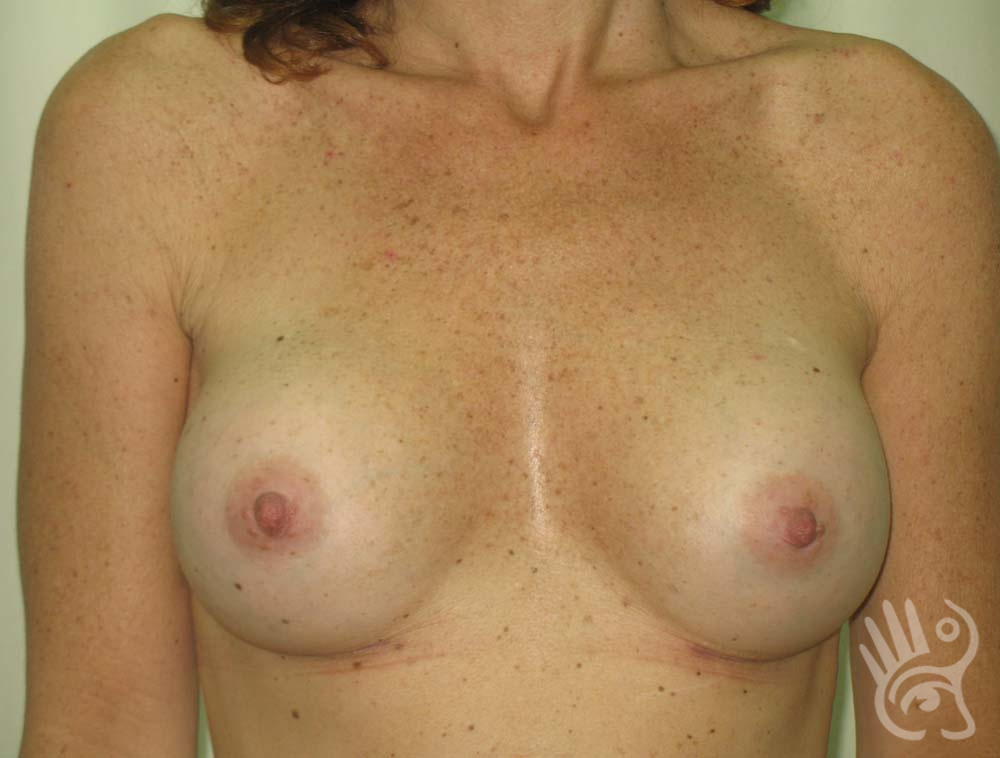
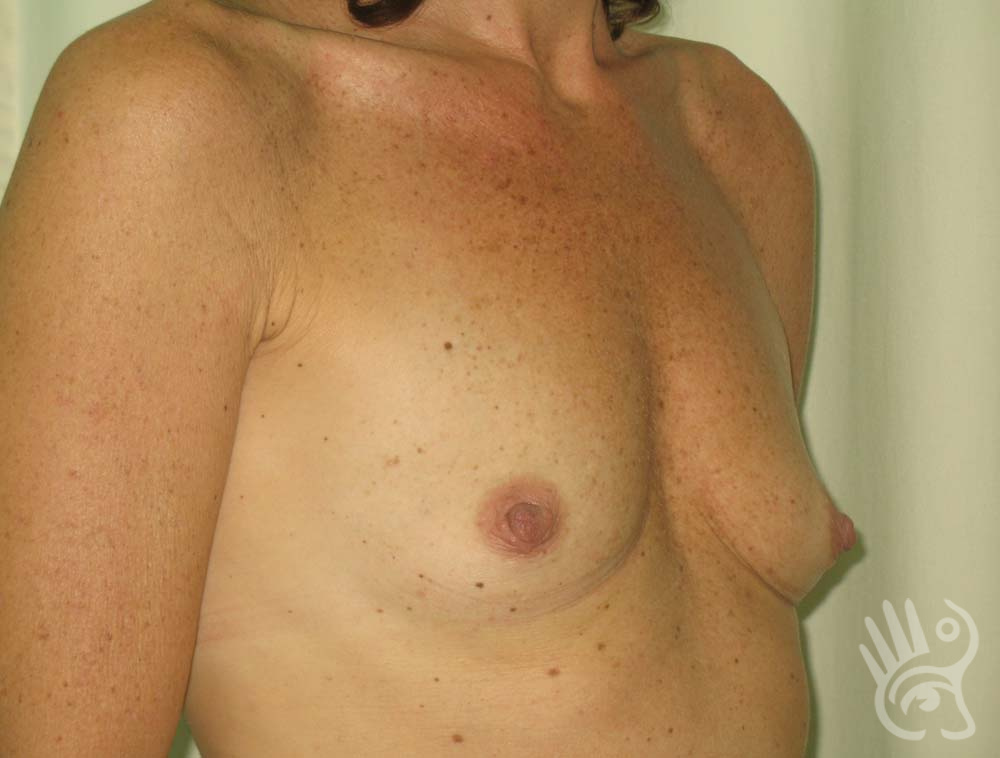
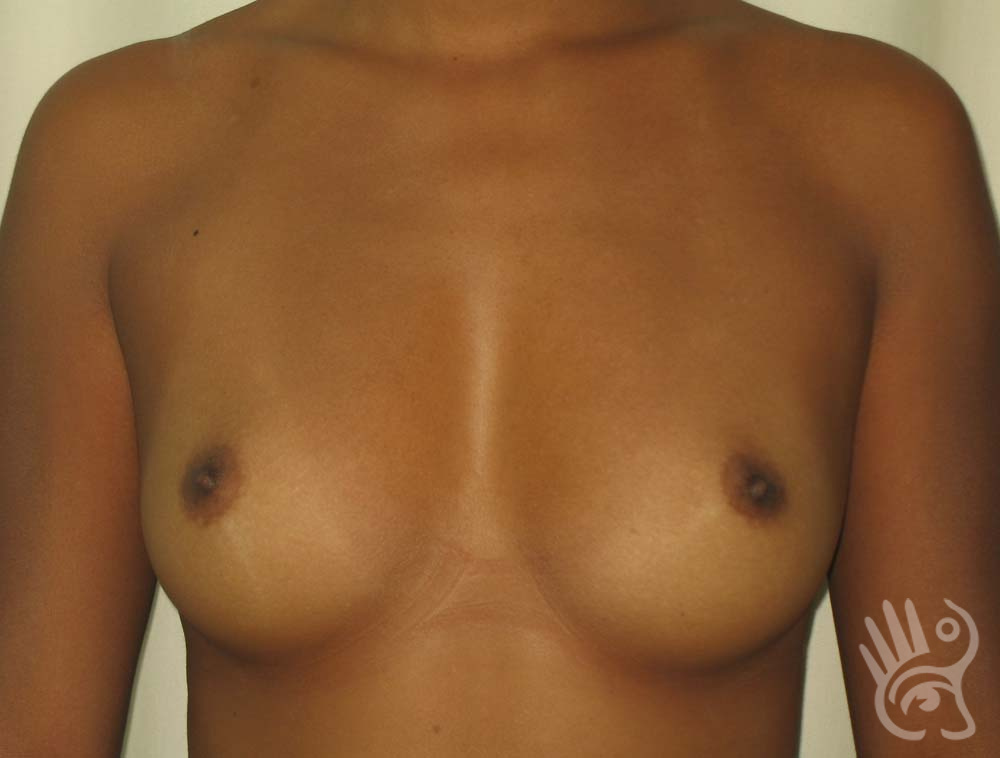
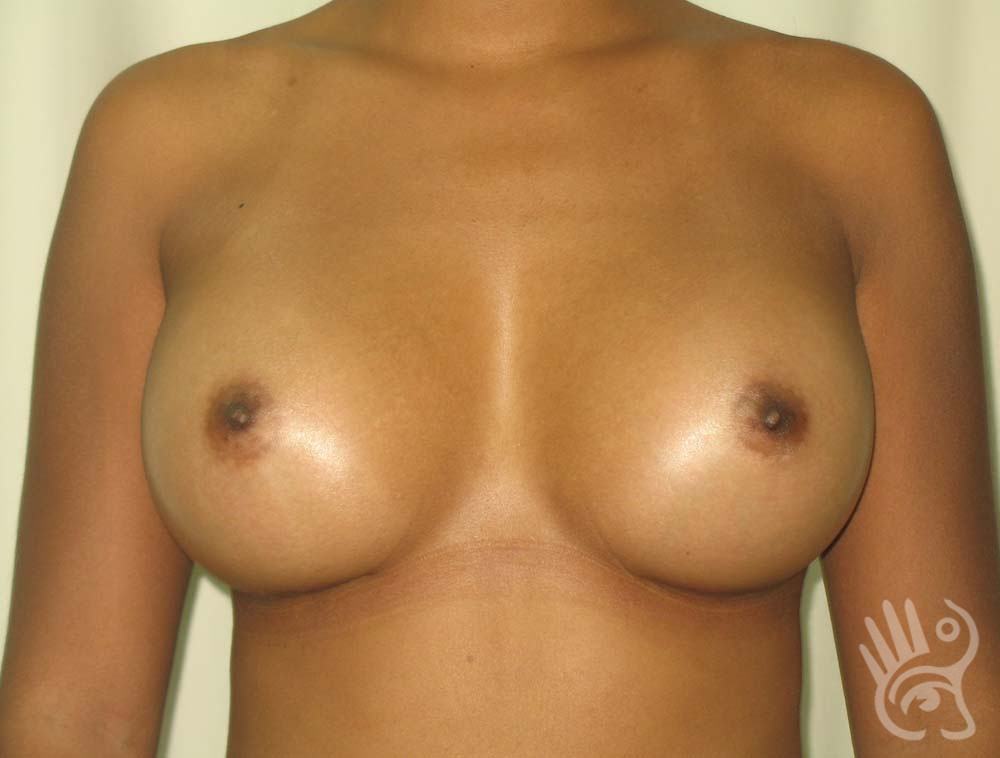
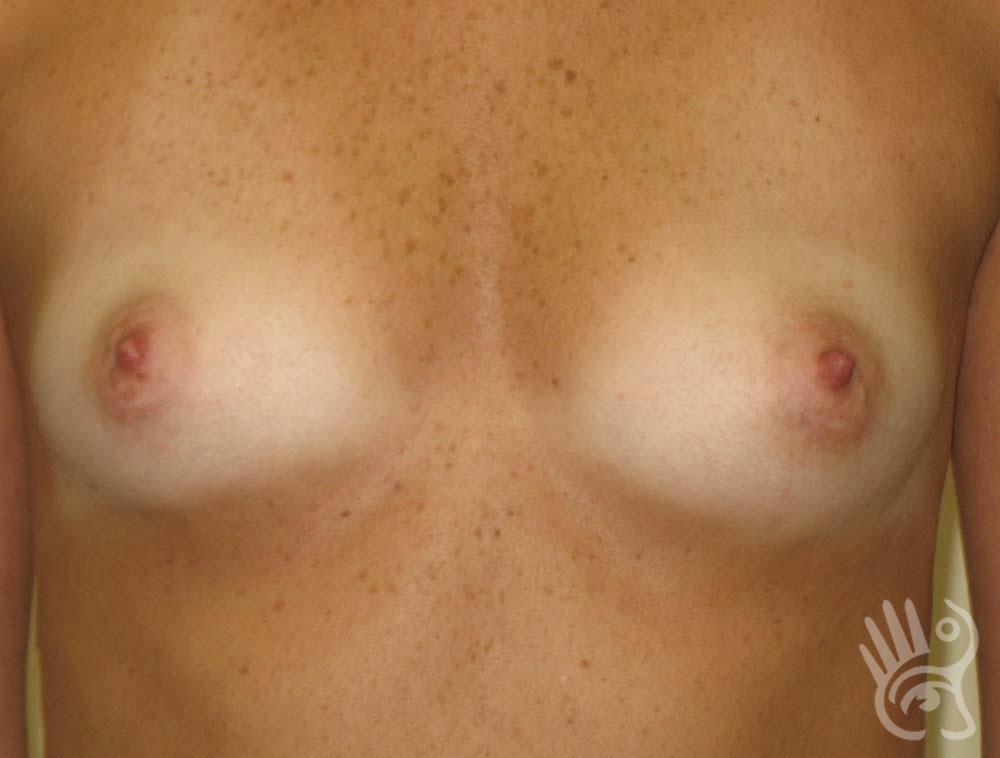
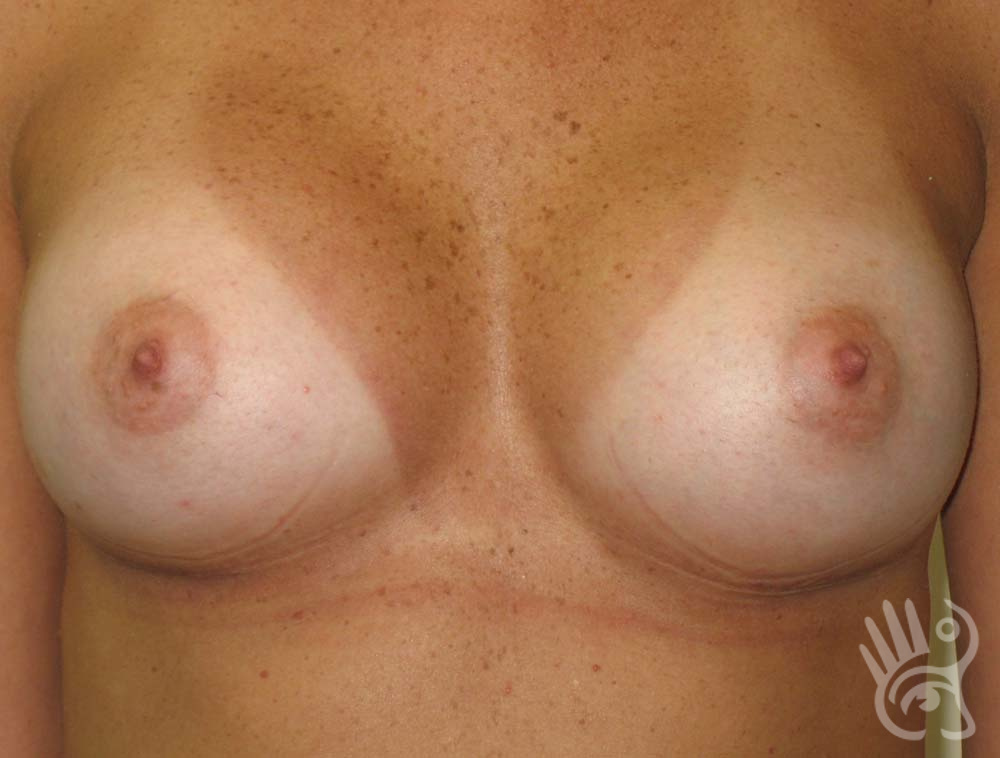
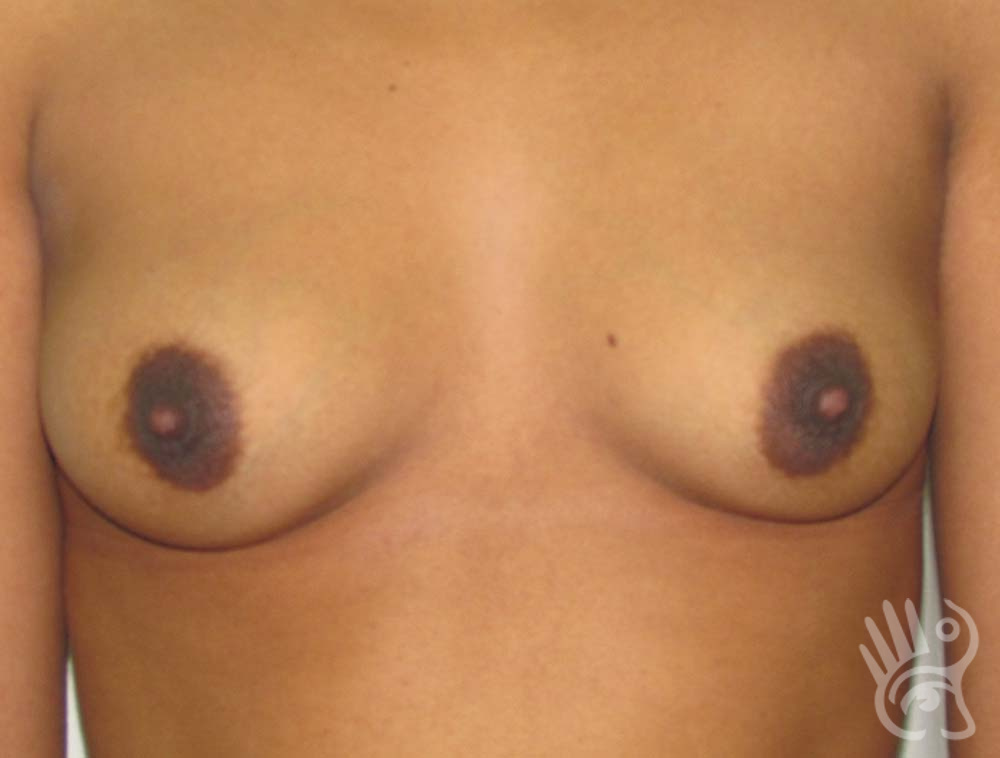
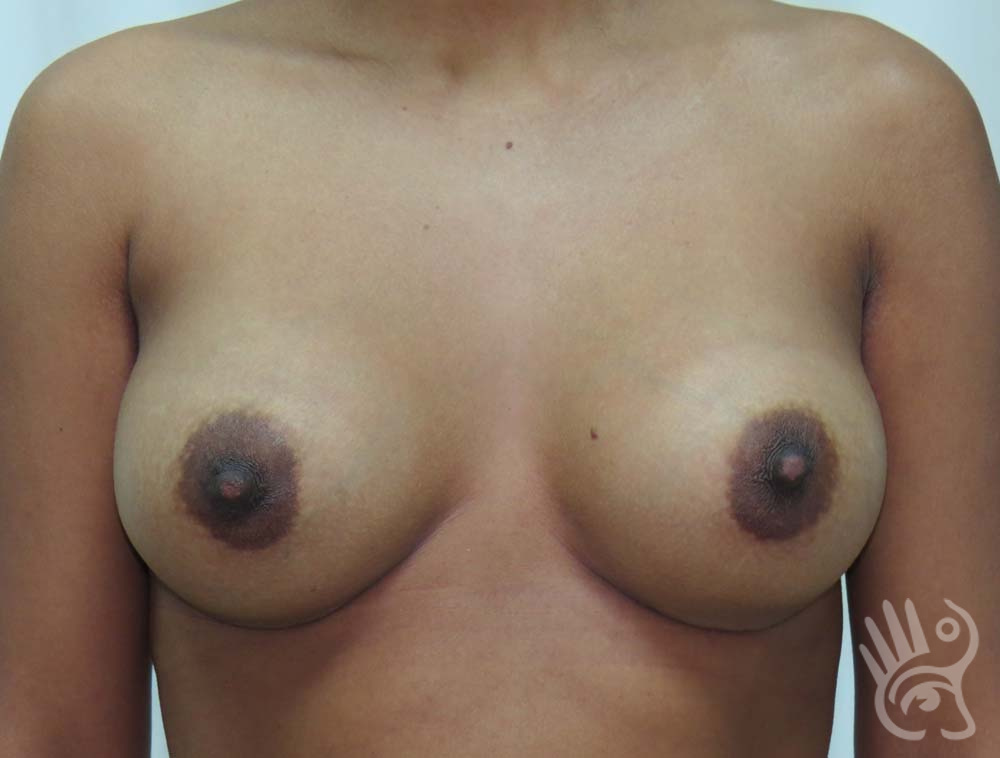
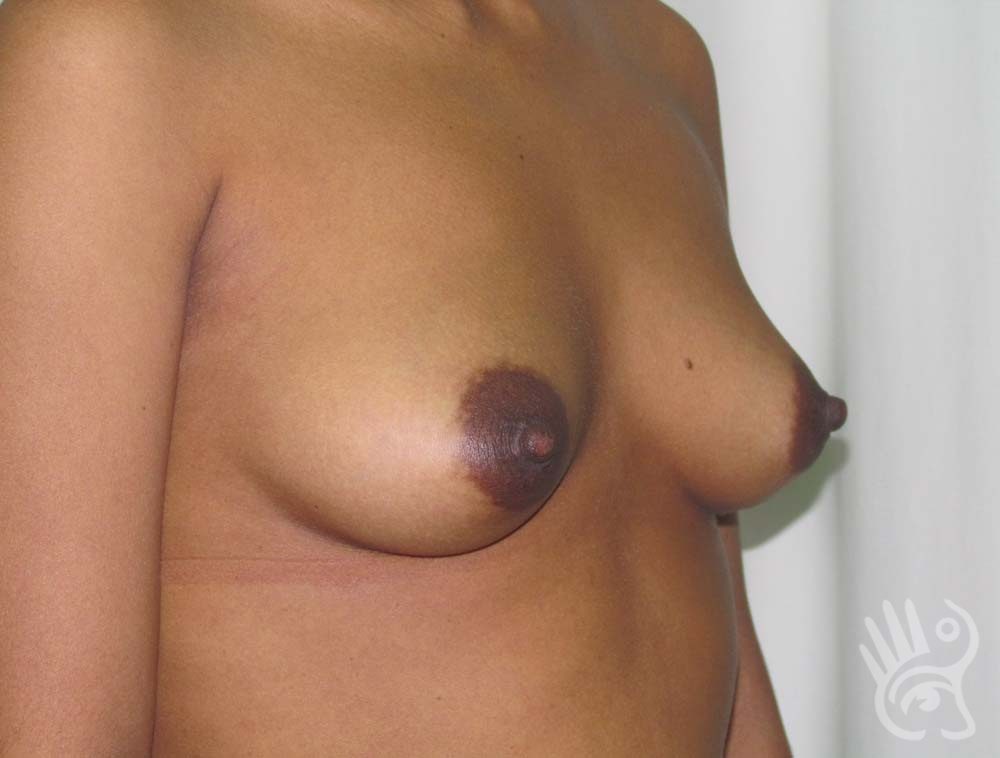
As with any other surgery, complications can arise with breast augmentation. A wound can bleed or an infection can occur. In rare cases, a prosthesis is ejected. The risk of complications is therefore present, but small. The scars may temporarily become red and thick after the procedure. In addition, impaired wound healing can cause a permanently wide scar. If the prosthesis hardens or the breast changes shape, it may be that the prosthesis has started to leak and must be replaced. There are also the normal risks of anesthesia. These risks are no greater or less than with any other procedure. The anesthetist will discuss this with you.
ALCL
A rare recently reported complication in breast implants is BIA-ALCL (Breast Implant Associated – Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma). This is not breast cancer, but a form of Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma (lymph gland cancer) that can occur in the capsule and fluid around the breast implant. You can recognize it by the relatively rapid enlargement of the breast due to fluid accumulation around the prosthesis or by getting a lump in the capsule around the prosthesis. ALCL is curable when the correct diagnosis and treatment are made in time. In a 2018 study, BIA-ALCL was investigated for the Netherlands. Women with breast implants have an increased risk of ALCL compared to women without breast implants. By the time a woman with a breast implant turns 50, the chance that she has contracted this disease is about 1 in 35,000. That will be 1 in 7,000 by the time she is 75 years old. In this study, as in other international studies, BIA-ALCL appears to be more common in implants with a coarse roughening of the shell, so-called macro-textured implants. Importantly, BIA-ALCL appears to occur in all types of implants, including implants with less rough or smooth surfaces and polyurethane-coated implants. The Health Care Inspectorate indicates that breast implants comply with the applicable regulations and that breast implants do not need to be removed preventively. As a result of the above publication from 2018, it is expected that follow-up research at European level will be launched to further substantiate these current recommendations.